Do you require any assistance? Simply reserve your appointment online below
Dequervains tenosynovitis
Patient Centered Care
Dequervains tenosynovitis is a painful condition affecting the tendons on the thumb side of your wrist. If you have dequervain’s tenosynovitis, it will probably hurt when you turn your wrist, grasp anything or make a fist.
Although the exact cause of de Quervain’s tenosynovitis isn’t known, any activity that relies on repetitive hand or wrist movement — such as working in the garden, playing golf or racket sports, or lifting your baby — can make it worse.
Signs and symptoms of Dequervains Tenosynovitis
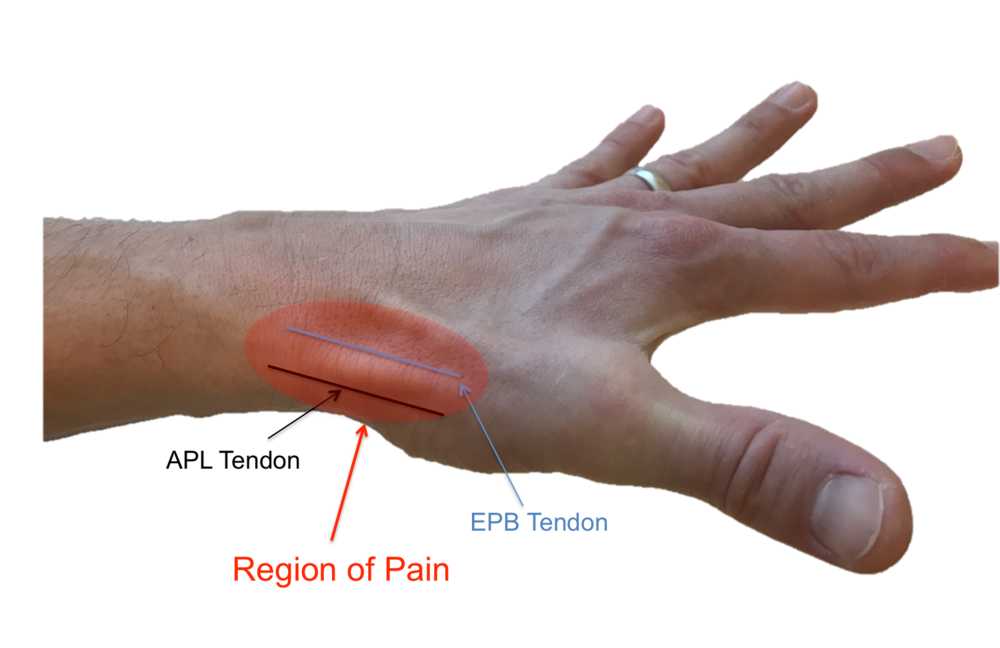
If the condition goes too long without treatment, the pain may spread further into your thumb, back into your forearm or both.
Pinching, grasping and other movements of your thumb and wrist aggravate the pain.
Symptoms of de Quervain’s tenosynovitis include:
Pain near the base of your thumb
Swelling near the base of your thumb
Difficulty moving your thumb and wrist when you’re doing something that involves grasping or pinching
A “sticking” or “stop-and-go” sensation in your thumb when moving
Risk factors
Risk factors for dequervain’s tenosynovitis include:
- Age. If you’re between the ages of 30 and 50, you have a higher risk of developing de Quervain’s tenosynovitis than do other age groups, including children.
- Sex. The condition is more common in women.
- Being pregnant. The condition may be associated with pregnancy.
- Baby care. Lifting your child repeatedly involves using your thumbs as leverage and may also be associated with the condition.
- Jobs or hobbies that involve repetitive hand and wrist motions. These may contribute to de Quervain’s tenosynovitis.

You are in Great Hands
Treatment of Dequervain’s Tenosynovitis

Treatment for Dequervain’s tenosynovitis focuses on reducing pain and swelling. It includes:
- Applying heat or ice to the affected area.
- Taking a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). These include ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) or naproxen (Aleve).
- Avoiding activities that cause pain and swelling. Especially avoid those that involve repetitive hand and wrist motions.
- Wearing a splint 24 hours a day for 4 to 6 weeks to rest your thumb and wrist.
- Getting injections of steroids or a local anesthetic (numbing medicine) into the tendon sheath. These injections are very effective and are used regularly.
A physical therapist or occupational therapist can show you how to change the way you move. This can reduce stress on your wrist. He or she can also teach you exercises to strengthen your muscles.
Most people notice improvement after 4 to 6 weeks of treatment. They are able to use their hands and wrists without pain once the swelling is gone.
Untreated de Quervain’s tenosynovitis might make it hard to use your hand and wrist properly and limit your wrist range of motion.