Do you require any assistance? Simply reserve your appointment online below
Discoid Meniscus Injury
We help you feel better
The menicus acts as a “shock absorber” between your femur (thighbone) and tibia (shinbone).
It protects the thin articular cartilage that covers the ends of the bones and helps the knee to easily bend and straighten.
There are two menisci in the knee: the medial meniscus on the inside of the knee, and the lateral meniscus on the outside
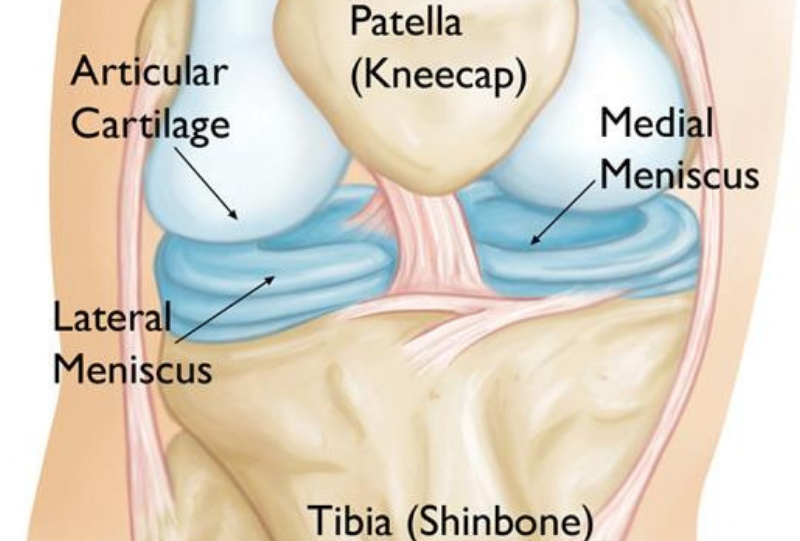
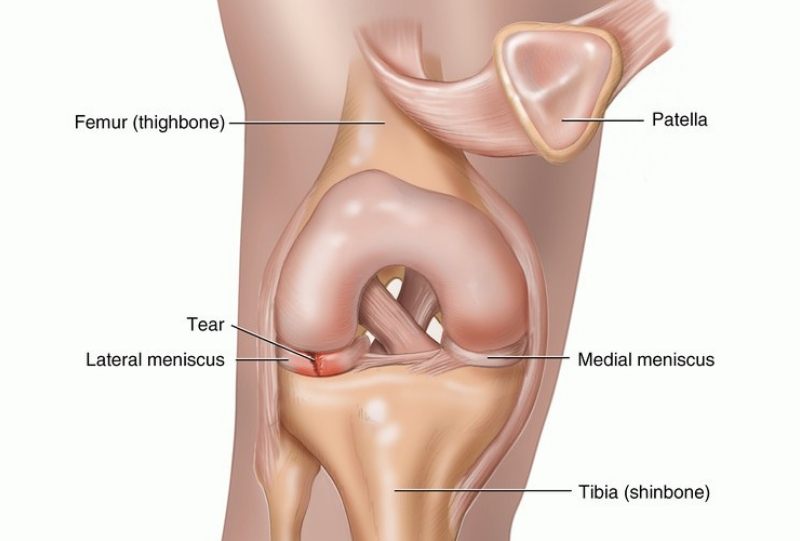
They are more prone to injury than a normal meniscus. The thick, abnormal shape of a discoid meniscus makes it more likely to get stuck in the knee or tear.
If the meniscofemoral ligament attachment to the tibia is also missing, the risk for injury is even greater.
Once injured, even a normal meniscus is difficult to heal. This is because the meniscus lacks a strong blood supply and the nutrients that are essential to healing cannot reach the injured tissues.
In many cases , patients experience symptoms without there being any injury to the meniscus.
Signs and Symptoms
Symptoms often begin during childhood. The most common symptoms of a discoid meniscus or torn discoid meniscus are:
Pain
Stiffness or swelling
Catching, popping, locking of the knee
- Feeling that the knee is “giving way”

Diagnosing Discoid Meniscus Injuries

After discussing your child’s medical history and any events that occurred before symptoms started, your doctor will examine your child’s knee.
Your child may or may not have tenderness where the bones meet.
During test, your doctor will twist your child’s knee with the knee bent and straightened. In many cases, there is a popping or clunking sensation.
In extreme cases, part of the meniscus will pop out of the knee joint and can be seen right under the skin.
Other tests include imaging tests such as X-rays and MRI scans.
Comprehensive treatment of Discoid Meniscus Injuries
Sometimes, a doctor discovers a discoid meniscus when evaluating the knee for a different problem. If It is not causing any symptoms, then specific treatment for it may not be necessary.
In case it is causing pain, popping, or other symptoms, however, your orthopedic surgeon will probably recommend arthroscopic surgery.

Enjoy a full range of motion
Surgical Treatment

Knee arthroscopy is one of the most commonly performed surgical procedures.
During arthroscopy, the surgeon makes a few small incisions around the knee and inserts a small camera, called an arthroscope, into the joint. The camera displays pictures on a television screen, and the surgeon uses these images to guide miniature surgical instruments.
Most arthroscopic surgeries are done on an outpatient basis. Patients usually go home a few hours after the procedure.
Treatment depends on the type of discoid meniscus.
- Complete and incomplete discoid meniscus with no tears are typically treated with saucerization, a procedure in which the meniscus is cut and re-shaped into a crescent.
- If the discoid meniscus is also torn, the surgeon may perform a saucerization and then trim away the torn portion. Some tears can be repaired with stitches, rather than removed.
- The hypermobile Wrisberg form of discoid meniscus is saucerized if necessary, then stabilized with stitches to sew the meniscus to the lining of the joint.

