Do you require any assistance? Simply reserve your appointment online below
Distal radius fractures (Broken Wrist)
Find relief for your pain
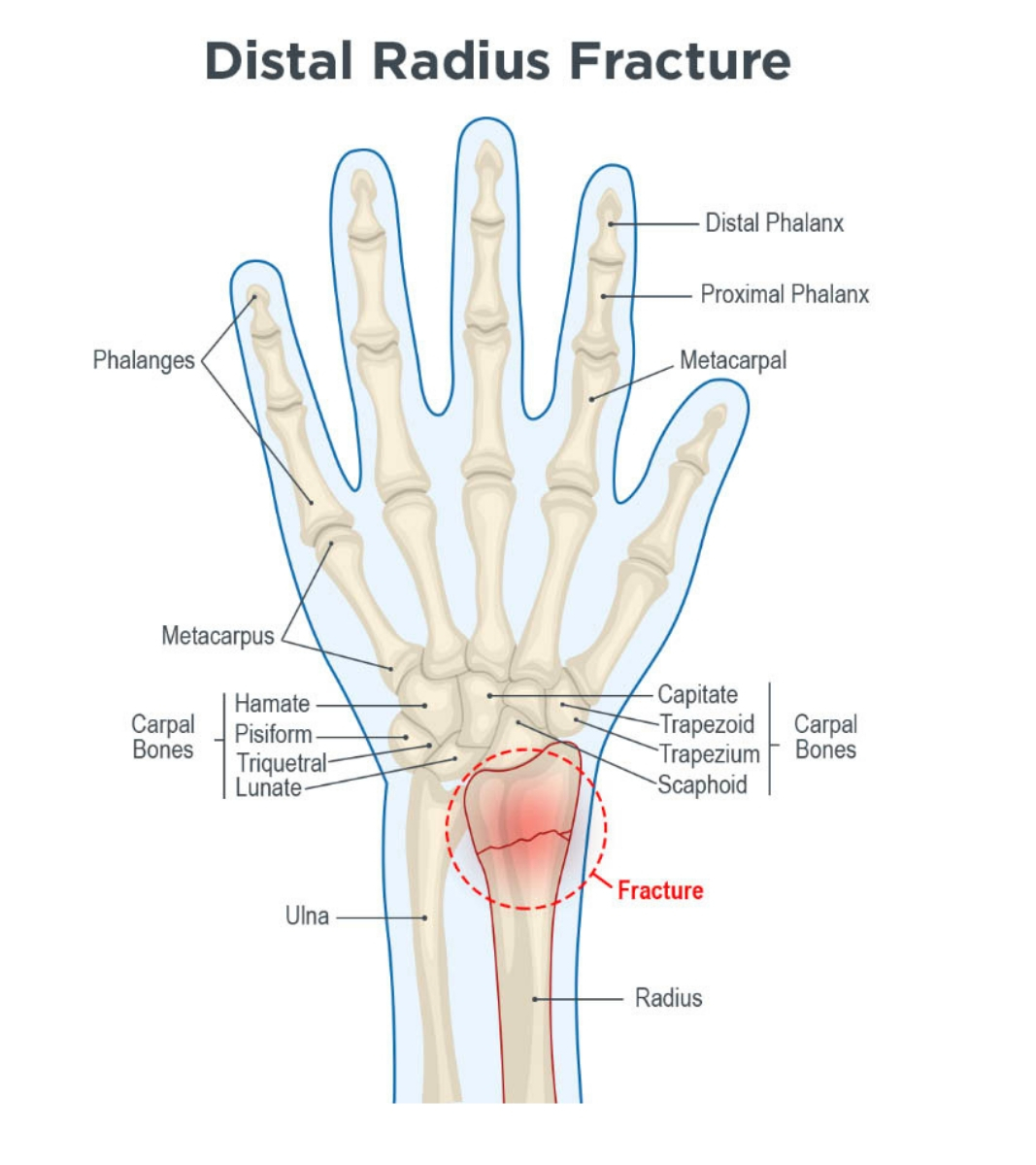
The radius is the larger of the two bones of the forearm. The end toward the wrist is called the distal end. A fracture of the distal radius occurs when the area of the radius near the wrist breaks.
Distal radius fractures are very common and always occurs about 1 inch from the end of the bone.
There are two common variants of distal radius fractures that are characterized by the direction of forces applied to the wrist during a fall:
- Colles’ fractures, the most common type of distal radius fractures, which occur when falling on an outstretched hand, where the hand is extended backward on the wrist, and
- Smith’s fractures, which are caused by the opposite mechanism, i.e., when the hand is flexed forward under the wrist.
Symptoms of a broken wrist

When you have a distal radius fracture, you will almost always have a history of a fall or some other kind of trauma.
You will usually have pain and swelling in the forearm or wrist. You may have a deformity in the shape of the wrist if the fracture is bad enough.
The presence of bruising (black and blue discoloration) is common. See your doctor if you have enough pain in your arm to stop you from using it normally.
Feel free to visit our ortho urgent care in Kenya if the injury is very painful, the wrist is deformed, you have numbness, or your fingers are not pink. You may want to protect the wrist with a splint and apply ice to the wrist and elevate it until you get to the doctor’s office.
Causes and risk factors associated with broken wrist
The most common cause of a distal radius fracture is a fall onto an outstretched arm.
Osteoporosis (a disorder in which bones become very fragile and more likely to break) can make a relatively minor fall result in a broken wrist.
Many distal radius fractures in people over 60 are due to osteoporosis if the fall was relatively minor such as a fall from a standing position.
A broken wrist can happen even in healthy bones, if the force of the trauma is severe enough. For example, a car accident or a fall off a bike may generate enough force to break a wrist.
How is a Broken wrist diagnosed?
Diagnostic methods that a physician may use to help diagnose a Distal Radius Fracture include:
- A thorough physical examination is important in identifying any noticeable deformities, swelling, contusions, in the radius/wrist. Individuals are also expected to provide an explanation of the circumstances that caused the injury. In addition to this, a complete medical history can aid in arriving at a definitive diagnosis
- X-rays are the most common method in evaluating a fracture, if the bone has been displaced. This diagnostic test helps provide a clear image of the bone, identify the exact location of the injury, and determine the extent of the fracture
- A CT scan takes a series of x-ray images from several different angles. These images are then merged to create cross-sectional images of bones and soft tissues of the arm/wrist and helps a physician evaluate the severity of the injury.
- A DEXA scan can also be recommended to assess for the presence of osteoporosis.

Possible complications of (distal radius fracture)Broken wrist
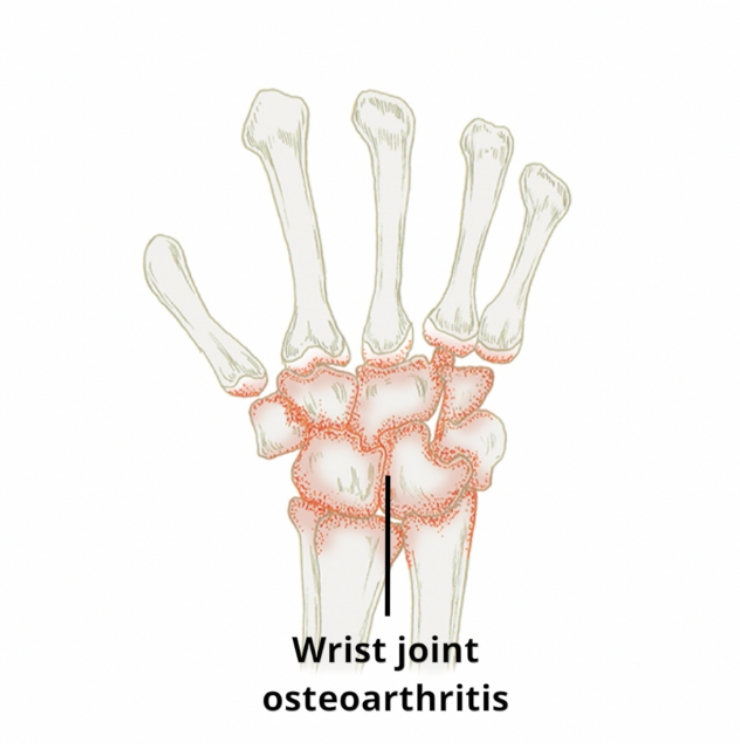
Complications associated with Broken wrist (Distal Radius Fracture) include:
- Permanent damage to certain nerves and blood vessels
Abnormal deformity of the wrist
- Degenerative joint disease (osteoarthritis)
Abnormal pressure build-up within the muscles of the arm/wrist that reduces blood flow, preventing oxygen and nourishment from reaching the nerve and muscle cells (termed as compartment syndrome)
You are in Great Hands
How is Broken wrist (distal radius fracture) treated?
Treatment of broken bones follows one basic rule: the broken pieces must be put back into position and prevented from moving out of place until they are healed.
Nonsurgical Treatment
If the broken bone is in a good position, a plaster cast may be applied until the bone heals.
If the position (alignment) of your bone is out of place and likely to limit the future use of your arm, it may be necessary to re-align the broken bone fragments.
“Reduction” is the technical term for this process in which the doctor moves the broken pieces into place. When a bone is straightened without having to open the skin (incision), it is called a closed reduction.
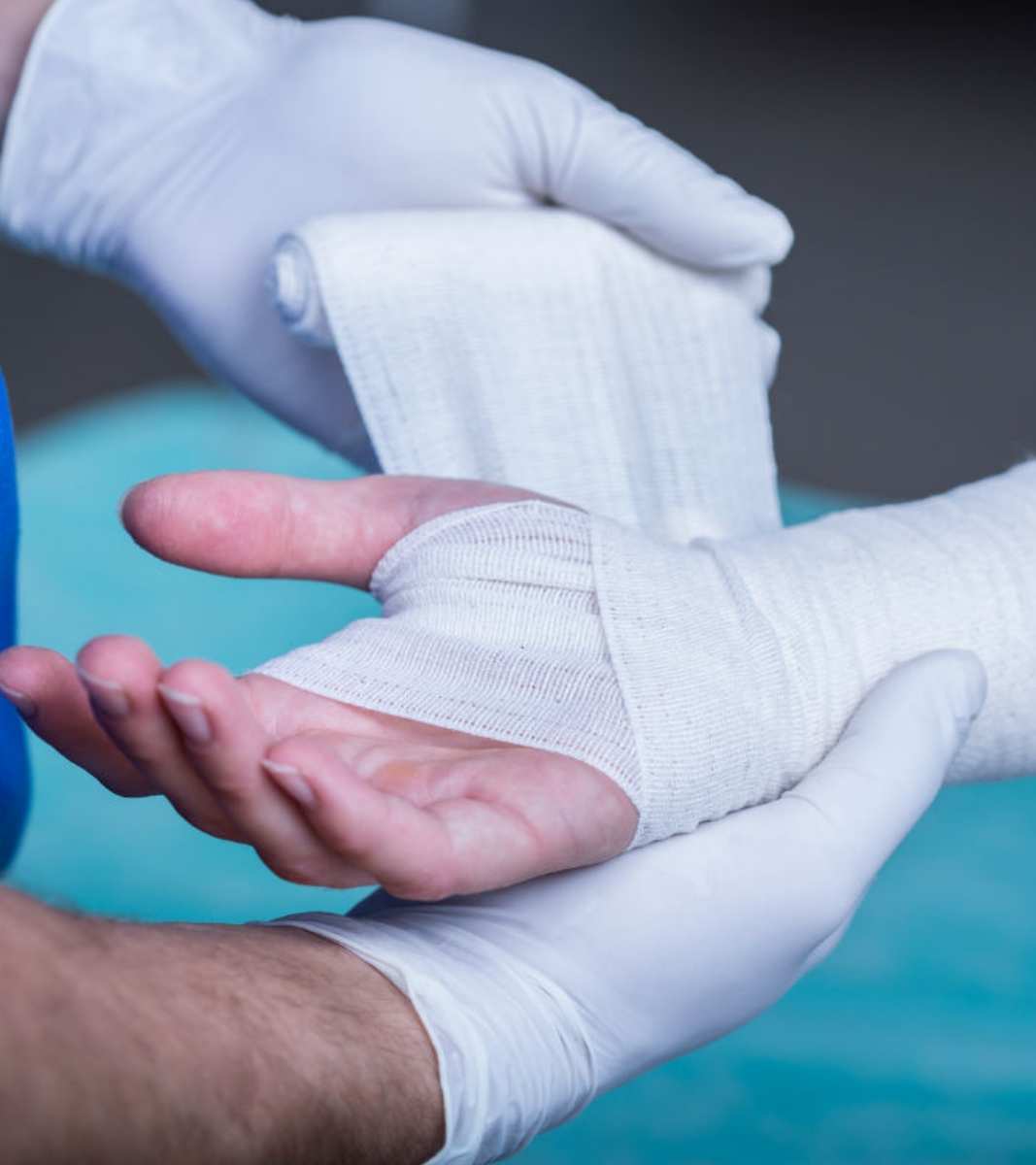

After the bone is properly aligned, a splint or cast may be placed on your arm. A splint is usually used for the first few days to allow for a small amount of normal swelling. A cast is usually added a few days to a week or so later, after the swelling goes down. The cast is changed 2 or 3 weeks later as the swelling goes down more, causing the cast to loosen.
Depending on the nature of the fracture, your doctor may closely monitor the healing by taking regular x-rays. X-rays may be taken less often if the fracture was not reduced and thought to be stable.
The cast is removed about 6 weeks after the fracture happened. At that point, physical therapy is often started to help improve the motion and function of the injured wrist.
Surgical treatment of a broken wrist
Surgical treatment methods for Broken wrist include:
- Closed reduction: Closed reduction is a surgical method that involves realigning the scaphoid bone back to its original position, without making an incision at the fracture site. This procedure is usually performed under a general anesthesia, or with conscious sedation using muscle relaxants
- Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF): Open reduction is a surgical procedure to realign the fractured bone, to its original position. Surgical hardware (such as plates, screws, or rods) is then used to stabilize the fractured bone under the skin
After surgery or casting, it is important that you achieve full motion of your fingers as soon as possible. If you are not able to fully move your fingers within 24 hours due to pain and/or swelling, contact your doctor for evaluation.
Your doctor may loosen your cast or surgical dressing. In some cases, working with an occupational or physical therapist will be required to regain full motion.

