Do you require any assistance? Simply reserve your appointment online below
Intoeing
Experts in children’s feet
An in-toeing gait is very common in children, and is a frequent complaint of many parents. In fact, an in-toeing gait (pigeon-toed) is the most common rotational deformity seen in pediatric orthopaedics.
Intoeing, also called “pigeon-toed”, is an abnormal condition characterized by the inward facing of the toe or feet instead of its straight alignment. You may observe this condition at an early age when your child starts walking.

Symptoms of intoeing
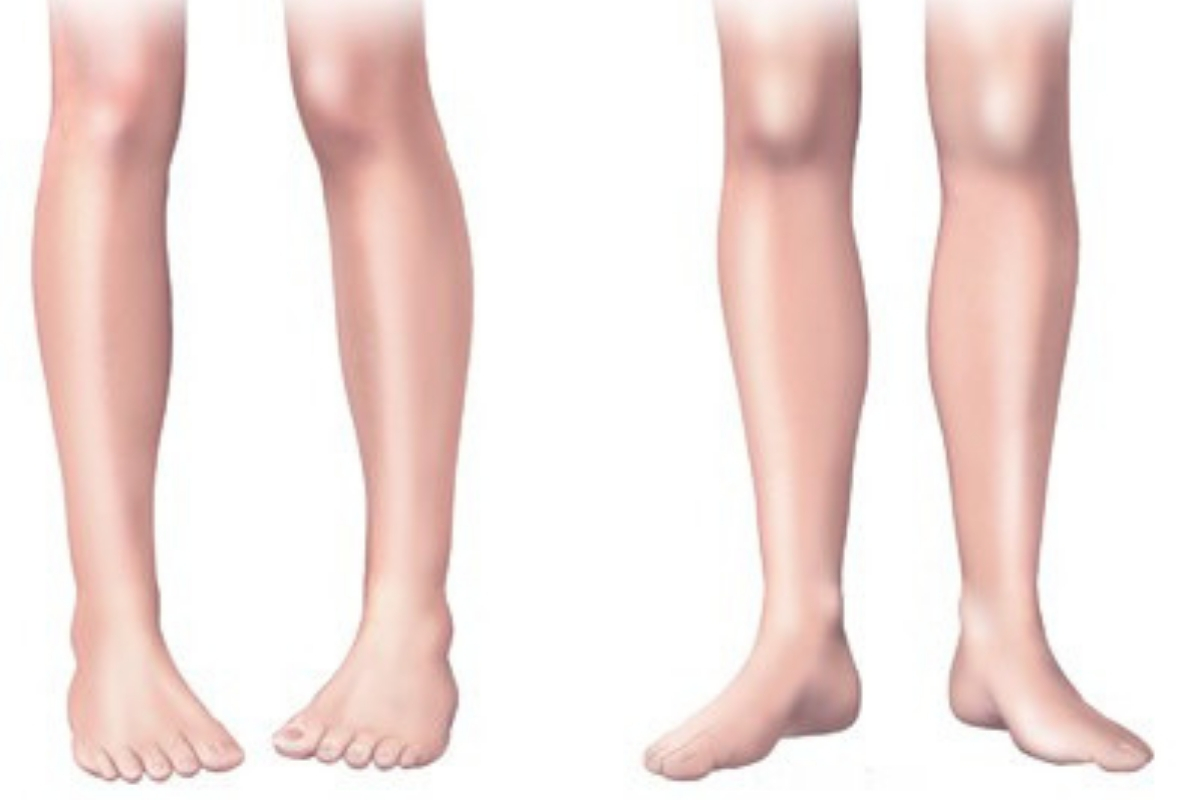
Intoeing is normally painless and does not cause arthritis, but may cause stumbling or tripping while walking or running. It usually corrects itself without any specific treatment by the age of 8 years.
Children having intoeing associated with any pain and swelling should be evaluated by an orthopedic surgeon.
Conditions that lead to intoeing
The types of intoeing depend upon the area involved in the misalignment.
- Metatarsus adductus (curved foot): In this condition, the foot of the child may bend inward from the middle to the toes.
- Tibia torsion (twisted shin): In tibial torsion, the lower leg (tibia) of the child is twisted inward. This abnormal rotation of the legs can occur before birth, to accommodate the baby in the limited space of the womb. The alignment of the lower legs may show gradual improvement after birth, with age, and may not require any specific treatment.
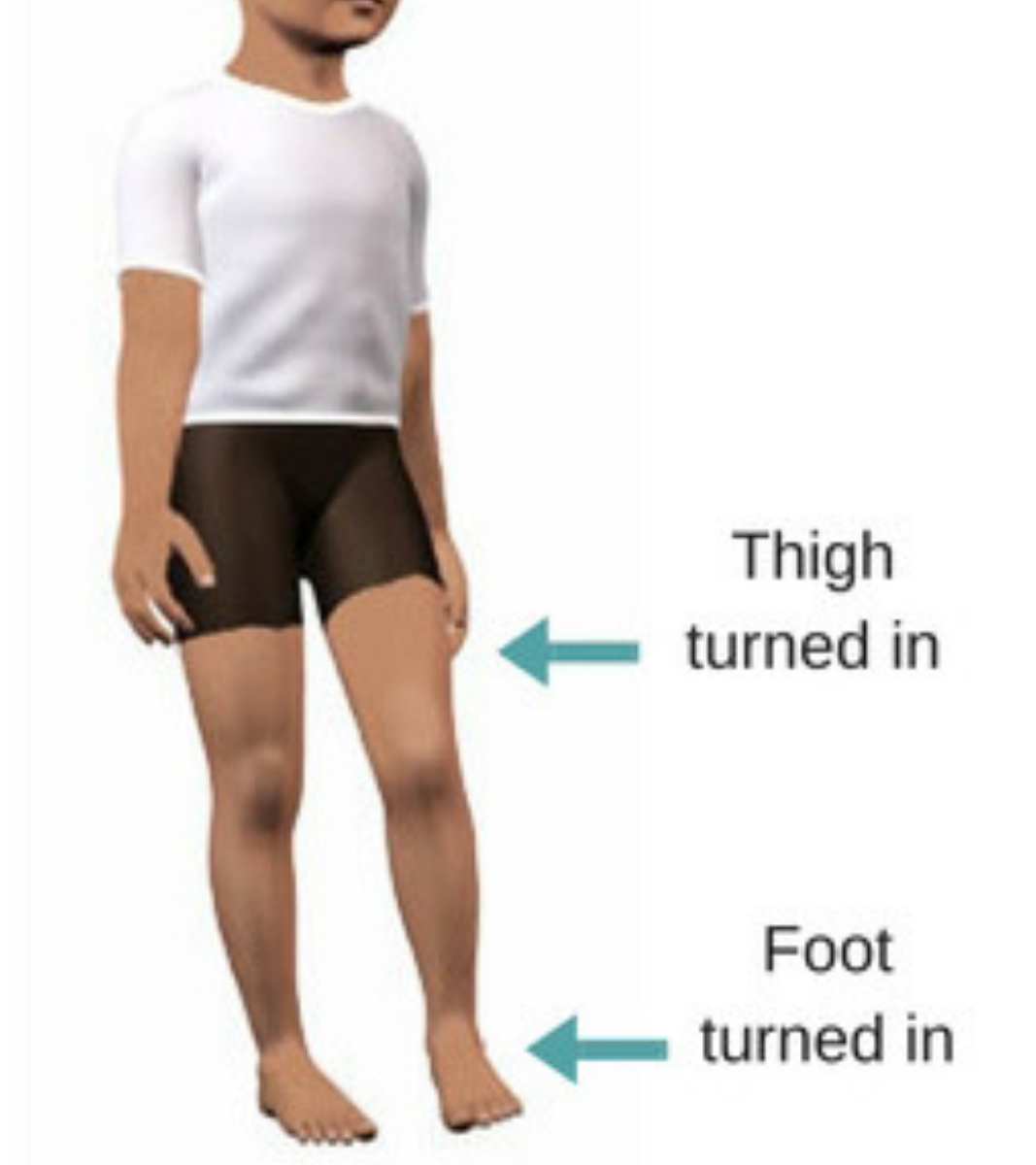
- Femoral anteversion (twisted thighbone): Also known as excessive femoral torsion, femoral anteversion is characterized by the abnormal inward bending of the thighbone, knees and feet while walking.
These conditions are inherent in nature that may occur individually or in association with other orthopaedic conditions. Due to the genetic involvement, such conditions cannot be prevented, only treated.
Diagnosis and evaluation of intoeing
The key to diagnosis is to determine what level in the leg the intoeing is occurring at.
Intoeing is evaluated by looking out for abnormal sitting positions.
Your doctor will take a thorough history, especially regarding birth history and developmental milestones. Any history of pain or limping should be discussed.
The physical exam will include watching your child walk and run, and checking range of motion of the hips, knees, ankles, and feet. He or she will also do a neurologic examination to check muscle tightness, nerve / muscle function, and coordination. He or she will also note whether your child has femoral anteversion, tibial torsion, or metatarsus adductus.
Personalized treatment of intoeing

There is really no specific treatment for increased femoral anteversion other than having the child avoid abnormal sitting positions. Encouraging the child to be involving in running and athletic activities is helpful.
Some people believe activity such as skating, which forces the leg into an externally rotated position, may be helpful.
Normal in-toeing in a toddler requires no treatment other than observation. It can take many years for the bones to untwist as the child grows . Special shoes, braces, or chiropractic manipulation do not make the intoeing improve any faster.

Increasing Comfort
More treatment options for intoeing

If the femoral anteversion or tibial torsion remains during middle school and cause problems with tripping or walking, surgery may be considered to cut and rotate the bone. This is very rarely needed in otherwise normal children who have femoral anteversion / tibial torsion.
Surgery is recommended to realign the shinbone or thigh bone in older children.
